DIABETES – EPIDEMIC OF THE 21ST CENTURY
Diabetes is a condition in which the pancreas can’t make enough insulin or the body can’t use the insulin produced efficiently. Insulin helps our bodies to produce glucose, a sugar which our bodies use for energy that comes from most foods we eat. With diabetes, glucose builds up in the blood, instead of being produced and delivered for energy production.
Of those with diabetes, 5% are Type 1 while 95% are Type 2 . The more serious Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease usually found in children or young adults. The immune system attacks the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas and destroys them. The pancreas then produces little or no insulin, preventing cells from taking up needed sugar from blood. Someone with type 1 diabetes needs daily injections of insulin and a strict diet with regular blood sugar monitoring under physician supervision.
 Type 2, or adult onset, is the more common form of diabetes and affects primarily adults over age 55, with about 80 percent being overweight. In type 2 diabetes, the pancreas usually produces insulin, but for different reasons the body can’t use the insulin effectively including primarily transfer into the cells. Glucose if not delivered into the cells where needed then builds up in the blood to produce unwanted excessive blood sugar levels.
Type 2, or adult onset, is the more common form of diabetes and affects primarily adults over age 55, with about 80 percent being overweight. In type 2 diabetes, the pancreas usually produces insulin, but for different reasons the body can’t use the insulin effectively including primarily transfer into the cells. Glucose if not delivered into the cells where needed then builds up in the blood to produce unwanted excessive blood sugar levels.
The symptoms of diabetes include feeling tired or ill, frequent urination, unusual thirst, constant hunger, weight loss, blurred vision, frequent infections, and slow healing of sores. High risk factors for developing diabetes High risk factors for developing diabetes include:
- Being more than 20 percent above your ideal body weight;
- Having immediate family with diabetes;
- Having high blood pressure of 140/90 or higher;
- Belonging to certain ethnic groups;
- Having low HDL, the good cholesterol; or high triglycerides
70 to 100 is now considered a normal blood sugar level, with 100 to 125 classified as prediabetic and over 126 being diabetes; the latter doubling your chance of death. A must in monitoring blood sugar status in the body is a resting Hb-A1c test that measures the percentage of glucose molecules clinging to your red blood cells for the past 90 days. A 5.0 level is normal. If you have had diabetes Type 2 for an extended time, a 7.0 level is sought while 5.0 for a non-diabetic. If higher you have too much sugar floating in your blood and are prediabetic or diabetic.
Diabetes treatment focuses on keeping blood sugar in a normal range daily. Your doctor can evaluate if you need diabetes drugs or insulin shots but measurement over time is necessary versus instant readings that can be reading a spike in insulin rather than your overall blood sugar level over time.
In diet, a low carbohydrate, restricted sugar diet combined with exercise with weight control helps control or diminish your diabetes. Most diabetics should restrict carbohydrate intake to less than 45 grams daily. Don’t skip meals and eat several small ones if your schedule allows. Many prepare small servings and keep them in serving-size containers to be used throughout the day. Weight control is essential and often can dramatically reduce diabetes symptoms and sometimes even produce a cure based on blood sugar measurements. DIABETIC DANGERS IN HEALTH Diabetes is in almost epidemic growth in the United States, having doubled in just 15 years. How serious is diabetes? Did you know diabetes is now the primary cause of blindness (retinopathy), kidney disease (nephropathy), amputations and nerve damage (peripheral neuropathy) in the U.S.? Negative lifestyle changes in recent years, including obesity and lack of exercise, are primary causes.
Additionally, 65% of diabetics die from a heart attack or stroke, contributing to cardiovascular disease being the primary cause of death in the U.S.
The good news is if you have diabetes it can in most cases be controlled to enable a normal lifestyle. If you are diagnosed as millions of others, follow these steps and the advice of your physician:
As stated before, have a hemoglobin A1C blood test quarterly to know your average blood sugar level over the previous 3 months. Most physicians consider a target level of 7.0 or below for extended-time diabetics, with 5.0 for non-diabetics. Your fasting blood sugar should be below 130, with a target of 70 to 100.
Cholesterol levels are especially important because of the relationship of high cholesterol to heart attack and stroke risks. LDL or bad cholesterol should be less than 100 for diabetics. If diabetic, blood pressure should be below 140/90, with a prescription drug such as Lisinopril often given to assist in blood pressure management. Realize Lisinopril has side effects that increase mucous production that can negatively affect sleep and voice quality.
A baby aspirin of 81 mg is frequently suggested daily for cardio protective effects in the blood unless taking blood thinners such as Warfarin or Heparin. Do not take in excess of a baby aspirin dosage unless advised by your physician. Excess aspirin, also known as acetylsalicylic acid, usage can raise unwanted liver enzyme levels so be aware. Kidney disease and renal failure are a major risk with angiotensin-converting enzymes, or ACE inhibitors, often prescribed for diabetics.
Your feet are often negatively affected by diabetes and are another risk area that your doctor will check with a device called a mono-filament that tests your nerves and sensation. Exercise positively improves insulin resistance and decreases blood sugar levels. With doctor approval, moderate exercise activities of 30 minutes daily are optimum.
 Be sure to have your eyes checked annually for diabetic retinopathy. An ophthalmologist will check your retina at the back of your eye for diabetic damage. Natural ingredients in supplements such as NSC Immunition Eye Care Formula nutritionally contribute beneficial nutrients and vitamins for your eyes to help address diabetic concerns.
Be sure to have your eyes checked annually for diabetic retinopathy. An ophthalmologist will check your retina at the back of your eye for diabetic damage. Natural ingredients in supplements such as NSC Immunition Eye Care Formula nutritionally contribute beneficial nutrients and vitamins for your eyes to help address diabetic concerns.
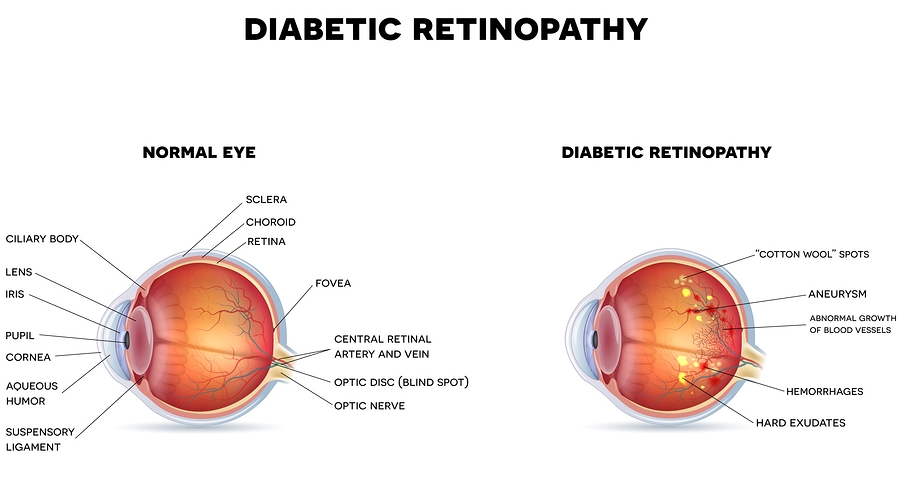
Acute complications of diabetes then include hypoglycemia, ketoacidosis, and hyperosmolar hypoglycemia (dehydration with 20% comas), while chronic complications are cardiovascular diseases, renal failure involving the kidneys, retinal damage in the eyes, nerve damage and poor healing. Be aware and make necessary lifestyle changes to avoid so many negative health challenges from diabetes. DIABETIC RETINOPATHY – EYE RISK Diabetic retinopathy is the most common diabetic eye disease that occurs when blood vessels in the retina change. Sometimes vessels swell and leak fluid or even close off completely. In other cases, abnormal new blood vessels grow on the surface of the retina.
The retina is a thin layer of light-sensitive tissue that lines the back of the eye. Light rays are focused onto the retina, where they are transmitted to the brain and interpreted as the images you see. The macula is a very small area at the center of the retina responsible for your pinpoint vision, allowing you to read or recognize a face. Diabetic retinopathy usually affects both eyes, with unchecked progression leading to vision loss that in many cases cannot be reversed. NPDR The first form of diabetic retinopathy is Non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy or NPDR. Many people with diabetes have mild NPDR, that doesn’t affect their vision. NPDR is the earliest stage of diabetic retinopathy in which damaged blood vessels in the retina begin to leak extra fluid and small amounts of blood into the eye. Sometimes, deposits of cholesterol from the blood may leak into the retina. NPDR can cause changes in the eye, including:
- Micro-aneurysms causing small bulges in blood vessels of the retina that often leak fluid.
- Retinal hemorrhages seen as tiny spots of blood that leak into the retina.
- Hard deposits of cholesterol or other fats from the blood.
- Macular edema seen asswelling or thickening of the macula caused by fluid leaking from the retina’s blood vessels. The macula doesn’t function properly when it is swollen and
- Macular ischemia where small blood vessels called capillaries close. Your vision blurs because the macula no longer receives sufficient blood to enable proper vision.
PDR The second form is Proliferative diabetic Retinopathy, or PDR, which occurs when many of the blood vessels in the retina close, preventing sufficient blood flow. In an attempt to supply blood to the area where the original vessels closed, the retina responds by growing new blood vessels called neo-vascularization.
Unfortunately, these new blood vessels are abnormal and don’t supply the retina with proper blood flow. The new vessels often appear with scar tissue that may cause the retina to wrinkle or detach. PDR can affect both central and peripheral vision. The best treatment for diabetic retinopathy is don’t get it. Strict control of your blood sugar and weight will significantly reduce the long-term risk of diabetic vision loss. NSC Eye-care Formula contains multiple eye nutritional aids with Lutein, B Vitamins and Eyebright plus Chromium and Red Raspberry to assist in normalizing blood sugar levels and Quercetin to reduce blood leakage in the retina. N Acetyl L Cysteine and Astaxanthin promote natural Glutathione production, while Zeaxanthin nutritionally enhances retina protection. RESEARCH – ORAL INTAKE OF BETA 1,3 GLUCAN NUTRITIONALLY HELPS REDUCE DIABETES RISKS Regarding diabetes and beta glucan, in a peer reviewed article (PubMed 27396408) on current research published in Molecular Nutrition & Food Research, researchers Y Cao, et al reported “B-Glucans have been shown to reduce the risk of obesity and diabetes.” The orally administered pure B-(1,3) glucan in mice significantly down-regulated the blood glucose through suppressing the sodium glucose cotransporter SGLT-1 expression in intestinal mucosa.

What is SGLT-1? SGLT-1 plays a major role in glucose absorption and incretin hormone release in the gastrointestinal tract. So what is incretin? Incretin hormones stimulate insulin secretion in response to meals potentially creating insulin spikes, while beta glucan nutritionally helps minimize insulin spikes by the suppression or minimization of incretin hormone release after a meal “Meanwhile, pure B-glucan promoted glycogen synthesis and inhibited fat accumulation in the liver…and depressed pro-inflammatory cytokines,” according to the report. Glycogen is the principal storage form of glucose in animal and human cells.
Excess glucose stored as glycogen can become a fat primarily around the middle (belly fat). Beta glucan increases the synthesis of glycogen or the breaking down of this complex compound; thus breaking down excess glycogen to enhance controlling obesity. Beta glucan usage must be combined with dietary changes and moderate exercise to lose excess weight so involved in creating diabetes. Weight loss is essential to diminishing Type 2 diabetes levels, including cure.
In additional peer reviewed research published in Vascular Health Risk Management ( PMD 19337540 ) researchers Chen and Raymond state, “The major risk [of diabetes mellitus] is vascular injury leading to heart disease, which is accelerated by increased lipid levels and hypertension. Management of diabetes includes: control of blood glucose level and lipids; and reduction of hypertension. Dietary intake of beta-glucans has been shown to reduce all these risk factors to benefit the treatment of diabetes and associated complications.”
NSC IMMUNITION DIABETES PACKAGE – 40% DISCOUNT!
NSC Diabetes Package Pkg Price Retail
NSC 100 Extra Strength – 30 ct $41.97 $ 69.95
NSC Eyecare Formula – 30 ct $14.97 $ 24.95
NSC Circulatory Plus – 180 ct $35.97 $ 59.95
Total Diabetes Pkg Price $92.95 $154.85
For Detailed Label/Ingredient Information click on the individual Product and then on Supplement Facts.